TheSchoolRun.com closure date
As we informed you a few months ago, TheSchoolRun has had to make the difficult decision to close due to financial pressures and the company has now ceased trading. We had hoped to keep our content available through a partnership with another educational provider, but this provider has since withdrawn from the agreement.
As a result, we now have to permanently close TheSchoolRun.com. However, to give subscribers time to download any content they’d like to keep, we will keep the website open until 31st July 2025. After this date, the site will be taken down and there will be no further access to any resources. We strongly encourage you to download and save any resources you think you may want to use in the future.
In particular, we suggest downloading:
- Learning packs
- All the worksheets from the 11+ programme, if you are following this with your child
- Complete Learning Journey programmes (the packs below include all 40 worksheets for each programme)
You should already have received 16 primary school eBooks (worth £108.84) to download and keep. If you haven’t received these, please contact us at [email protected] before 31st July 2025, and we will send them to you.
We are very sorry that there is no way to continue offering access to resources and sincerely apologise for the inconvenience caused.
What is a formula?
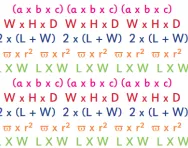
What is a formula?
A formula is a group of mathematical symbols and numbers that show how to work something out.
Examples include formulae for calculating the perimeter and area of 2D shapes and how to work out the volume for 3D shapes.
Formulae are also used to convert measurements, for example from kilometres to miles or temperatures from ºC to ºF.
How does a formula help children in maths?
A formula tells you which measurements or facts you need to solve a calculattion, and how to calculate the measurement or information you need. There are different formulae for different things.
For example, the formula to calculate the volume of a cuboid is W x H x D = V³ (the width multiplied by the height multiplied by the depth equals the volume, which we record in cubic units), where each symbol has a mathematical meaning.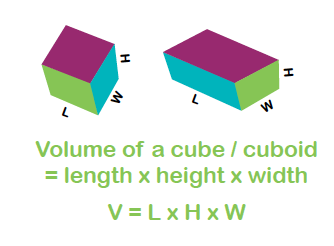
- W means width
- H means height
- D means depth
- V means volume
- ³ means cubed
- = means equals
You can use the same formula to calculate the volume of any cuboid.
How and when primary children are taught mathematical formulae
Children will be familiar with many of the symbols used in formulae (such as + x and =) from Year 1, but it is not until Year 6 that children are formally introduced to the concept of a formula.
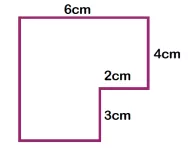
Children will be expected to be able to use a range of different formulae to calculate the perimeter and area of 2D shapes and volume of 3D shapes. For example:
Shape: square
How to calculate the perimeter: 4 x side
How to calculate the area: side²
How to calculate the volume: Cube: w³
Shape: rectangle
How to calculate the perimeter: 2 x (L + W)
How to calculate the area: L x W
How to calculate the volume: Cuboid: W x H x D
Shape: triangle
How to calculate the perimeter: Side + side + side (a x b x c)
How to calculate the area: (b x h) ÷ 2
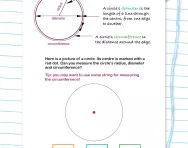
Shape: circle
How to calculate the perimeter: 2 x π x r
How to calculate the area: π x r²
Regular polygon: perimeter is calculated as n x l
In the formulae the symbols represent the following:
L = Length W = Width H = Height D = Depth B = Base π = pi (3.14) r = radius n = number of sides
When learning to apply forumlae in calculations children will be given a diagram of a shape with the measurements needed marked on. Their task is to apply the measurements to the correct formula to calculate the required answer.
For example:
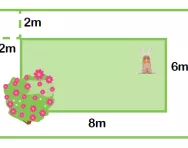
Using the formula W x H x D can you find out the volume of this cuboid?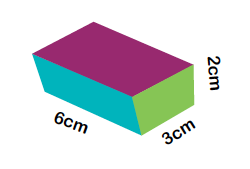
The answer is 6 x 3 x 2 = 36cm³