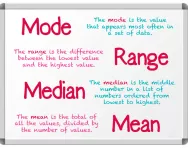
What are mode, mean, median and range?
We explain the meaning of the terms mode, mean, median and range, with examples of how to find each of these from a set of numbers, as well as examples of the types of questions primary-school children might be asked when interpreting data sets.
What is rotation of shapes?
We explain what the term rotation means in geometry, how primary-school children are taught to rotate shapes clockwise or anticlockwise or about the centre, and how to combine rotation with coordinates.
What is translation of shapes?
We explain what the term translation means in primary-school geometry and how children are taught to translate a shape on squared paper and to combine coordinates with translation of shapes.
What are equivalent fractions and simplifying fractions?
We explain what equivalent fractions are, how the concept of equivalence is introduced in primary school maths and how knowledge of equivalent fractions is then used to simplify fractions.
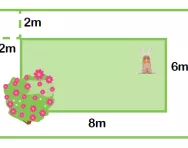
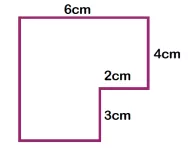
What is area?
We explain what the term area means and how children are taught to calculate the area of a shape.
What is the perimeter?
We explain what the perimeter is and how teachers explain the concept to children in KS2, as well as showing the types of perimeter word problems children could be faced with.
What are multiples and factors?
We explain what multiples and factors are and how children are taught to recognise multiples from Year 1 and factors from Year 5, with examples of the types of problem they might be asked to solve.
What are standard and non-standard units?
We explain what standard and non-standard units are and how non-standard units can help children understand the concept of weight before they master the skill of accurate measurement and converting units of measurement
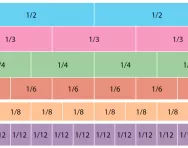
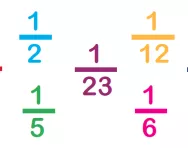
What are unit fractions?
We explain what unit fractions are and why children need to understand the concept of unit fractions before moving onto more advanced fractions learning.
What is symmetry?
We explain what symmetry is and how primary-school children are taught to find the line of symmetry and draw lines of symmetry on different shapes.
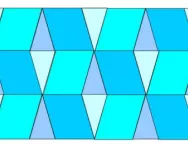
What are tessellating shapes?
We explain what tessellating shapes are and why tessellation may be taught in primary school as part of learning about 2D shapes.
What is an estimate?
We explain how children are taught to make estimates to check whether their answers are correct and how this skill is applied to more difficult calculations as your child advances through primary school.
What are probability / chance / likelihood?
We explain what probability / chance / likelihood means, how children are taught about probability from Year 5 and the kinds of mathematical problems involving probability they might be asked to solve.
What is proportion in maths?
We explain what proportion is and how children are taught about proportion from Year 4, giving examples of the kinds of problems involving proportion they might be asked to solve.
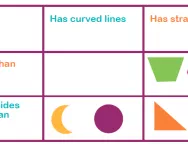
What is a Carroll diagram?
We explain what a Carroll diagram is and how primary-school children are taught to use a Carroll diagram to sort data, such as a group of objects or numbers, methodically.
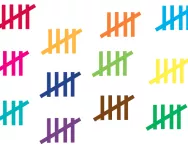
What is a tally chart?
We explain what a tally chart is and how children are taught to use a tally chart to collect data and interpret data on tally charts.
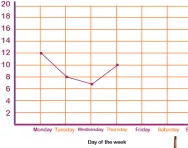
What is a line graph?
We explain what a line graph is and how children are taught to construct line graphs and answer questions on a line graph.
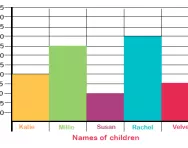
What is a bar chart?
We explain what a bar chart is and how children are taught to interpret a bar chart, produce their own bar charts on grid paper and on a computer, and produce bar charts with grouped discrete data.
What are coordinates?
We explain what coordinates are and how children are taught to read and plot coordinates on a grid.
Memory aids for kids
Rhymes, acrostics and other mnemonics could all help your child to remember important facts, from tricky spellings to grammar rules. We asked the experts why they work so well – and for their top 10 memory aids.
Glue ear: all your questions answered
Children afflicted by glue ear can have a miserable time at school, but the nature of the condition means many parents and teachers may not even guess that a child is suffering. Moira Holden looks at the causes of glue ear and how it can be treated.
Best construction toys for kids
Want to develop your child’s problem-solving skills, understanding of physics and fine motor control (essential for handwriting)? Time to get out the building blocks! We pick eight of the best construction toy sets for budding engineers, architects and designers.
100 of the best educational toys: KS2
Your child will be having so much fun playing these games they won't even realise they're practising their times tables, improving their vocabulary, boosting mental maths skills and revising geography facts. Hands-on fun is guaranteed with every learning activity, from writing in hieroglyphics to dissecting a body and observing the night sky.
100 of the best educational toys: stocking fillers
Don't forget the stockings! These little toys and games are the perfect size to slip in, yet still offer plenty of educational opportunity. Encourage observation, curiosity, dexterity and creativity with these brilliant gifts, whatever age your child is.
What is rounding numbers?
We explain what the term 'rounding numbers' means and how children are taught to go from rounding two-digit numbers in Year 2 to rounding decimals in Years 5 and 6.
What is ratio?
We explain what ratio is and how children in KS2 are taught to solve problems involving ratio.
What is the bus stop method for division?
We explain what the bus stop method for division or short division is and why this is a quick and efficient method for working out division with larger numbers.
What is chunking?
We explain what chunking is and how this division technique is taught in primary school to help your child divide large numbers.
Primary-school Chinese: the lowdown
Learning a foreign language has been compulsory for Key Stage 2 children since 2014, and Mandarin is an option in forward-thinking schools. Lucy Dimbylow explains what you need to know about Chinese in primary schools.
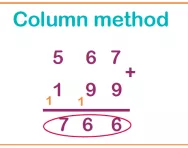
What is the column method?
We explain what the column method is, how it is set out and why it is an efficient method for working out addition and subtraction.
School exclusions: everything primary-school parents need to know
Parents faced with their child being excluded from school are often very upset and confused. Moira Holden looks at the regulations that surround the exclusion process.
13 ways to make grammar fun for children
With all Year 6 children required to take a spelling, punctuation and grammar test and more emphasis on the technical side of English in the primary curriculum, we asked the experts for their top tips and practical activities to help your child engage with – and enjoy – grammar.
How to help your child develop study skills
Learning how to study, complete homework projects and revise is essential as your child moves towards the end of primary school. We asked the experts for their advice on getting into good work habits. By Lucy Dimbylow
6 primary-school health concerns parents need to look out for
The days of colic and cradle cap may be long gone, but your primary school child is now susceptible to a different range of health issues. From tummy bugs and nits to emotional health concerns, Lucy Dimbylow looks at what you need to know to keep them safe and well.
7 life skills all primary-school children need
Not everything your child needs to get on in life can be learned in the classroom. From typing and DIY skills to cooking and lifesaving, here are seven vital skills that will stand them in good stead in the primary-school years and beyond. By Lucy Dimbylow
Philosophy in primary school: how thinking skills will benefit your child
Pondering life’s big questions could have some surprising benefits for your child. So how is philosophy taught in primary schools, and how can you encourage children to think deeper at home?
What are the four operations?
We explain what the four operations are and how children learn about addition, subtraction, multiplication and division over KS1 and KS2, working towards solving problems involving all four operations.
What are regular and irregular shapes?
We explain what regular and irregular shapes are and suggest mnemonics to help children remember how many sides different shapes have. We also have examples of the types of questions primary-school children might be asked about shapes.
What are the properties of 2D and 3D shapes?
We explain what the properties of 2D and 3D shapes are, what faces, edges and vertices are and how children will describe 2D and 3D shapes in KS1 and KS2.
What are the names of 2D and 3D shapes?
We explain what the different 2D and 3D shapes are, when primary-school children are taught to name them and sort shapes according to their properties and when they learn to identify and draw their own nets of 3D shapes.