Year 1 articles
What is chunking?
We explain what chunking is and how this division technique is taught in primary school to help your child divide large numbers.
100 of the best educational toys: KS1
These games and toys consolidate early reading skills, help with simple maths calculations, boost strategic thinking and even introduce your KS1 child to engineering and geology! For literacy and numeracy fun in toy form, these are the games to try.
Primary-school Chinese: the lowdown
Learning a foreign language has been compulsory for Key Stage 2 children since 2014, and Mandarin is an option in forward-thinking schools. Lucy Dimbylow explains what you need to know about Chinese in primary schools.
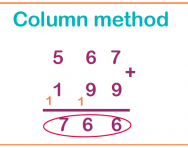
What is the column method?
We explain what the column method is, how it is set out and why it is an efficient method for working out addition and subtraction.
School exclusions: everything primary-school parents need to know
Parents faced with their child being excluded from school are often very upset and confused. Moira Holden looks at the regulations that surround the exclusion process.
13 ways to make grammar fun for children
With all Year 6 children required to take a spelling, punctuation and grammar test and more emphasis on the technical side of English in the primary curriculum, we asked the experts for their top tips and practical activities to help your child engage with – and enjoy – grammar.
6 primary-school health concerns parents need to look out for
The days of colic and cradle cap may be long gone, but your primary school child is now susceptible to a different range of health issues. From tummy bugs and nits to emotional health concerns, Lucy Dimbylow looks at what you need to know to keep them safe and well.
7 life skills all primary-school children need
Not everything your child needs to get on in life can be learned in the classroom. From typing and DIY skills to cooking and lifesaving, here are seven vital skills that will stand them in good stead in the primary-school years and beyond. By Lucy Dimbylow
Philosophy in primary school: how thinking skills will benefit your child
Pondering life’s big questions could have some surprising benefits for your child. So how is philosophy taught in primary schools, and how can you encourage children to think deeper at home?
What are the four operations?
We explain what the four operations are and how children learn about addition, subtraction, multiplication and division over KS1 and KS2, working towards solving problems involving all four operations.
What are regular and irregular shapes?
We explain what regular and irregular shapes are and suggest mnemonics to help children remember how many sides different shapes have. We also have examples of the types of questions primary-school children might be asked about shapes.
What are the properties of 2D and 3D shapes?
We explain what the properties of 2D and 3D shapes are, what faces, edges and vertices are and how children will describe 2D and 3D shapes in KS1 and KS2.
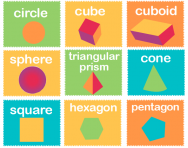
What are the names of 2D and 3D shapes?
We explain what the different 2D and 3D shapes are, when primary-school children are taught to name them and sort shapes according to their properties and when they learn to identify and draw their own nets of 3D shapes.
What is expanded notation?
We explain what expanded notation means, how it is taught in primary school and how it can help children with addition and multiplication calculations.
What are mathematical investigations?
We explain what types of mathematical investigations children will carry out in primary school and give examples of complex investigations they might be asked to solve in KS2.
What are analogue and digital?
We explain what analogue and digital are and how and when children are taught to read clock faces and convert between analogue and digital times in primary school.
What are time intervals?
We explain what time intervals are and how children are taught to work out time intervals in KS1 and KS2 maths.
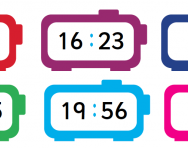
What are the 12-hour and 24-hour clock?
We explain how primary-school children are taught to use the 12-hour and 24-hour clock to tell the time on analogue and digital clocks, and how you can support their learning at home.
What are axes?
We explain what axes are and how your child will be taught to use axes on pictograms, bar charts and graphs.
What are arrays?
We explain what arrays are and give examples of how they can help children with their times tables learning and to explain the relationship between multiplication and division.
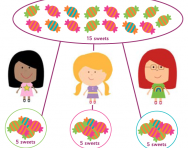
What is 'shared between'?
We explain what the term 'shared between' means and give examples of typical division problems your child might be set in KS1 and KS2.
What are clockwise and anti-clockwise?
We explain what clockwise and anti-clockwise means and give examples of typical exercises your primary-school child might be presented with to test their understanding of rotation.
What are equations?
We explain what equations are and how children are taught to solve equations in KS1 and KS2, as well as how the topic of algebra is introduced.
What are odd and even numbers?
We explain what odd and even numbers are and how primary-school children are taught about this concept in KS1 and then have to apply this learning in KS2.
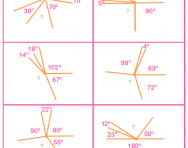
What are degrees?
We explain what degrees are and how children are taught to use protractors to measure angles, as well as reviewing the different knowledge children acquire about angles throughout KS1 and KS2.
What are right, acute, obtuse and reflex angles?
We explain what right, acute, obtuse and reflex angles are and how children are taught about different angles through KS1 and KS2.
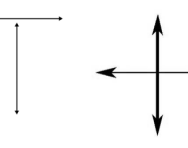
What is horizontal?
We explain how primary-school children are taught to recognise horizontal lines in shapes.
What is vertical?
We explain how primary-school children are taught to recognise vertical lines in shapes, and what you can to to support your child's understanding at home.
What is parallel?
We explain what parallel means and how children are taught about shapes throughout KS1 and KS2.
What is perpendicular?
We explain what perpendicular means and how children are taught angles throughout KS1 and KS2.
What is diagonal?
We explain what diagonal means in geometry and why it is important that children understand this term when learning about 2D shapes in primary school.
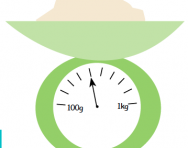
What is mass?
We explain what mass means, how mass is usually measured and how children are taught to convert from one unit of mass to another.
How do you 'convert into the same units'?
We explain what the phrase 'convert into the same units' means, how children are taught to convert units of measurement and techniques that teachers use to help children master this skill.
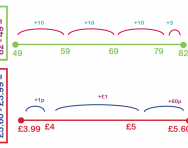
What is 'the difference between'?
We explain what teachers mean when they talk about finding 'the difference between' and give examples of how children are taught to work out the answers to subtraction problems.
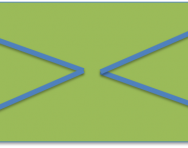
What is < and >?
We explain what the symbols < and > mean and give examples of how the concept is explained to primary-school children.
What is descending order?
We explain what descending order means and give examples of how the concept might relate to numbers, decimals, fractions or amounts of money.
What is ascending order?
We explain what ascending order means, how children are asked to sort into ascending order in primary school and give examples of how the concept might relate to numbers, dates, decimals or alphabetical lists.
What is repeated addition?
We explain what repeated addition means, how it is taught in school as a foundation of multiplication understanding and techniques that teachers use to help children grasp the concept.
What is a number sentence?
We explain what a number sentence is and how primary-school children are taught to write number sentences (or fill in gaps in number sentences) in KS1 and KS2.
What is a sum?
We explain what a sum is and how children are taught to understand the term when it appears in mental maths tests, word problems or investigations.